Barnegat Bay is home to several species of crabs, but the Blue crab is the most common and sought after.
Crabs Crustaceans
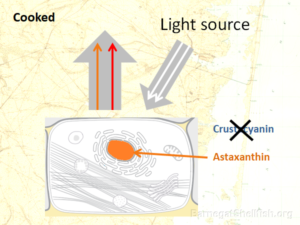
Why do crabs (and othe shellfish) turn red when you cook them?
First , a little science….
Crabs are usually brownish, bluish to olive green when alive and/or in the wild
Astaxanthin – a naturally occurring carotenoid found in microalgae
Carotenoid – organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae (.e.g. β carotene)
Crustacyanin – a protein that encloses astaxanthin and its light-absorption properties are changed.
Crabs have a pigment called astaxanthin in their shells. Astaxanthin is a carotenoid pigment: absorbing blue light and appearing red, orange or yellow in color.
While the animal is alive, astaxanthin lies wrapped in the tight embrace of a protein called crustacyanin.
The protein holds the pigment so tight that it is flattened and its light-absorption properties are changed.
The astaxanthin-crustacyanin complex then winds up giving off a blue-green color.
A closer look at the cells that make up the exoskeleton (click on image to expand) 

Other crustaceans are effected by the same astaxanthin/crustacyanin protein coloration as crabs.
These include lobsters, crawfish (crayfish) and shrimp.
Lobsters and crawfish are like crabs, when boiled their shells turn red. With shrimp there is a little bit more to the story.
 Shrimp color will vary from one species to another being almost transparent in Grass Shrimp Palaemonetes pugio .
Shrimp color will vary from one species to another being almost transparent in Grass Shrimp Palaemonetes pugio .
The meat color of raw shrimp can range from white to shades of gray.
Astaxanthin is the primary color pigment in many shrimp, and it helps provide their tissue (not just the shell) with its pink, red and orange shades.
 While many reddish-orange foods get their color from other carotinoids, shrimp are especially concentrated in this one particular type of carotenoid. Astaxanthin often accounts for at least two-thirds of all carotenoids in shrimp.
While many reddish-orange foods get their color from other carotinoids, shrimp are especially concentrated in this one particular type of carotenoid. Astaxanthin often accounts for at least two-thirds of all carotenoids in shrimp.
 Flamingos are tall, pink wading birds with downturned bills.
Flamingos are tall, pink wading birds with downturned bills.
The color of flamingos is white to grayish white.
A large part of their diet (varies with location) consists of blue-green algae and brine shrimp.
In the digestive system, enzymes break down carotenoids into pigments that are absorbed by fats in the liver and deposited, for flamingos, in the feathers and skin.
(astaxanthin is freed from crustacyanin and eventually gets to the feathers)
Taking it a step further….. (while we’re on the subject)
Deciduous trees leaves are green during the growing season, colorful in the fall and bare branches in winter.
Fun Fact: The color model red green blue (RGB) colors when they are combined create white light.
 After the summer solstice, days shorten and winter is cold, dry and not as much sun to help give plants energy.
After the summer solstice, days shorten and winter is cold, dry and not as much sun to help give plants energy.
Instead of trying to keep their leaves, deciduous trees drop their leaves and seal the spots on the branches where the leaves had been attached.
Pigments play a big role here as well…..
 Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll
Essential in photosynthesis, allowing plants to absorb energy from light.
Chlorophyll absorb light most strongly in the blue portion of the electromagnetic spectrum as well as the red portion. It is a poor absorber of green and near-green portions of the spectrum, which it reflects, producing the green color of chlorophyll-containing tissues
 Xanthophyll
Xanthophyll
The yellow pigment of the leaves and are classified as accessory pigments which absorbs the wavelength that chlorophyll cannot absorb.
They are a subclass of carotenoids containing oxygen (oxygenated) They absorb blue light and serve as protection from excessive amount of sunlight to prevent further damage in the plant.
 Carotenoids
Carotenoids
The orange color could also be due to Carotenoids as well. The the hydrocarbon subclass (containing no oxygen). β-Carotene is one of the more common carotenoids existed in plants.
It can strongly absorb green and blue color, reflecting yellow and red light leading to its orange appearance.